Taizhou Pinsum Furniture Co.,Ltd , https://www.pinsumchina.com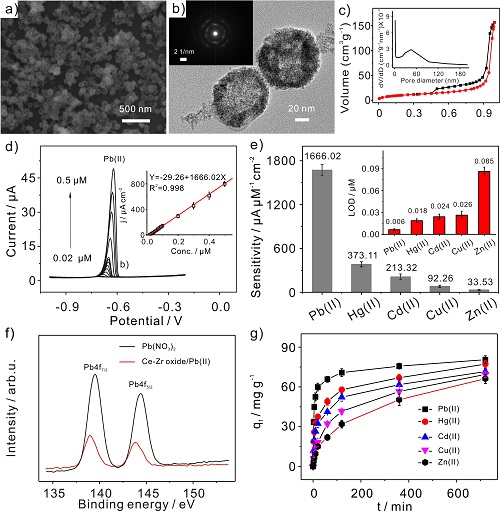
High-sensitivity and high-selectivity detection of Pb(II) in wastewater has progressed
China Instrument Network Instrument Development Recently, the research team of Huang Xingjiu, a researcher at the Hefei Institute of Technology, Hefei, Anhui Province, used a hierarchical porous yttrium-zirconium double-metal oxide nanomaterial to achieve high sensitivity to micro-pollutants, Pb(II), due to differences in adsorption rates of different heavy metal ions. Highly selective detection. This work has important scientific significance for realizing the selective and accurate detection of heavy metal ions in actual water samples. The relevant results have been published in Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical Journal of Elsevier (Sensors and Actuators B. 2017.11.061).
a) SEM images of Ce-Zr oxide nanomaterials; b) TEM images of Ce-Zr oxide nanomaterials; c) Adsorption-desorption curves and pore size distributions of Ce-Zr oxide nanomaterials in N2; d) The anodic stripping voltammogram of Pb(II) was measured with Ce-Zr oxide modified electrode; e) The comparison of sensitivity and detection limit of several different heavy metal ions was detected; f) After Pb(II) was adsorbed on Ce-Zr oxide nanomaterials High resolution XPS spectra; g) Study on the adsorption rates of different heavy metal ions for Ce-Zr oxide nanomaterials.
At present, although electrochemical methods have been widely applied to the detection of heavy metal ions and many research results have been obtained, when heavy metal ions are detected by elution voltammetry (such as Cu(II), Hg(II), Pb(II) , Cd(II), Zn(II)), different heavy metal ions can form intermetallic compounds and the adsorption of different heavy metal ions on the surface of the modified electrode during the enrichment process will generate competition, thus making simultaneous detection In the case of heavy metal ions, the interference between them is severe and it is impossible to accurately detect certain heavy metal ions. Therefore, it has always been a challenging and meaningful task to search for selective and accurate detection of a specific heavy metal ion.
In response to the above problems, researchers in the research group used graded porous cerium-zirconium double-metal oxide nanospheres (Ce-Zr) as electrode materials to study the Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres in detail by virtue of their adsorption of heavy metal ions. The anodic stripping voltammetric behavior of the heavy metal ions was measured at the electrochemically sensitive interface. The results show that the proposed method can achieve high sensitivity, high selectivity and high anti-interference detection of Pb(II). At the same time, the researchers studied the possible mechanism of selective detection of Pb(II) by Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres in combination with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) technology and a large number of adsorption experiments. The results show that the adsorption rates of different heavy metal ions on the surface of Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres are very different. In a short period of time (< 150 s), Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres react with Pb (II). The adsorption capacity is much larger than that of other ions, but due to the short electrochemical detection time, the amount of target material adsorbed on the surface of the electrode material determines the level of the electrochemical dissolution signal and adsorbs more during the enrichment phase of the elution voltammetry analysis. The Pb(II) thus reduces the deposition of more Pb(0) onto the electrode surface, which in turn results in an enhanced electrochemical signal during the dissolution process. Therefore, the electrochemically sensitive interface constructed by Ce-Zr oxide nanospheres can realize highly sensitive and selective detection of Pb(II). Finally, the proposed method was used to detect the Pb(II) in the inlet water sample of Hefei Wangtang Wastewater Treatment Plant, and obtain accurate test results and satisfactory recovery rate, indicating that the analytical method can detect the pollutants in the actual water sample. Pb (II) application potential.
The research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Innovation Crossing Team of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Dean’s Fund of the Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences.
(Original title: The Institute of Intelligent Research advances the accuracy and accuracy of high-sensitivity, high-selectivity, accurate detection of Pb(II) in wastewater.