In hydrometallurgical system, one of the problems most frequently encountered are precipitated oxidative leaching of sulfide minerals in solution and metal sulfide. Therefore, the dominant area map of the S-H 2 O system is of great significance in hydrometallurgy. It is known that in the S-H 2 O system, only S Θ , H 2 S(aq), HS - (aq), S 2 - (aq), SO 4 2 - (aq) and HSO 4 - are thermodynamically stable. The components. Other known sulfuric acid-containing salts and their salts are in a metastable state. These sulfuric acids include sulfurous acid H 2 SO 3 ; thiosulfuric acid H 2 S 2 O 3 ; dithionous acid H 2 S 2 O 4 ; H 2 S 2 O 6 and polysulfate H 2 S n O 6 . Further, both the alkali metal sulfide M 2 S and the hydrosulfide MHS form polysulfides of the general formula M 2 S n which contain an unbranched anion S n 2 - . The thermodynamic data of many of these metastable compounds can be obtained from the literature, and the relationship between them can be examined as an advantageous region map, in which sulfuric acid and its derived ions are not considered. First, free energy data The free energy data required to map the dominant regions of the S-H 2 O system are listed in the table below, along with the acid dissociation equilibrium and redox balance involved. For convenience and clarity, the numbering of each equilibrium equation is consistent with the number of the equilibrium line it represents on the dominant area map. Table S-H 2 O system, free energy generation substance S 2 - HS - H 2 S(aq) SO 4 2 - HSO 4 - H 2 O(1) △G Θ ∕kJ +111.4 +12.08 -27.83 -744.53 -755.91 -237.129 Second, the acid dissociation constant The component H 2 SO 4 does not exist in the solution reflected in the dominant zone map, only the following acid dissociation reactions occur: The lgK 2 value in the above formula has been taken 14 in the past, but later studies have found that even the presence of trace amounts of oxygen can cause the oxidation of alkali metal sulfides to produce various products ranging from elemental sulfur to sulfates. The H 2 S(aq) dissociation constant determined by the method produces a large error. Moreover, the classical method for determining the hydrogen ion activity, the acid dissociation constant, cannot be used to measure the H 2 S(aq) dissociation constant, which can poison the hydrogen electrode and the glass electrode. The H 2 S(aq) secondary dissociated bone number obtained by measuring the hydrogen ion activity with a low alkali error glass electrode was lgK 2 = -17.39. Third, redox balance Fourth, the advantage zone map and its analysis The acid decomposition equilibrium and the redox equilibrium formula are plotted on the Eh-pH diagram under the condition that all sulfur-containing substances have a activity of 10 -1 or 10 -4 to obtain the dominant region of the S-H 2 O system. . Each line in the figure corresponds to an equilibrium reaction, representing a two-phase equilibrium line. Activity 10-1 or 10-4, respectively, -1 and -4 are denoted by the corresponding line. Figure 1 S-H 2 O dominant area map (298K, S and H 2 S activities are 10 -1 or 10 -4 respectively ) Under these conditions there is a stable zone of elemental sulfur. That is, a 0.1 mol ∕L sulphate solution is reduced at a pH between 1.96 and about 7.7 to produce elemental sulphur. A lower than pH = 1.96 equilibrium is established between HSO 4 - and elemental sulfur. As the potential is lowered to a more negative value, the elemental sulfur in the pH = 6.99 H2S will be produced by the reduction HS is generated at higher pH -. Of course, in practice the ratio of HSO 4 - to SO 4 2 - and the ratio of H 2 S(aq) to HS - will change correspondingly to their pK values ​​as they undergo a pH change. This is indicated by a zone line on the Bucher corrosion map, where the substance changes its morphology, such as H 2 S(aq) to HS − , HSO 4 - becomes SO 4 2 - and Fe 3 + , becomes Fe 2 + or the like, and its total activity does not change. In Figure 1, the two equilibrium ions are equal in activity, and the three equilibrium lines meet at one point. This can also be used to verify that the calculations and plots are accurate. At a pH above about 7.7, there is a direct conversion between SO 4 2 - and HS - in 0.1 mol of ∕L solution. This higher pH limit of the sulfur stable zone is not very affected by the higher SO 4 2 - and HS - activity. For a solution with a concentration of 1 mol ∕L, the pH limit is only increased to 8.4. However, the presence of a sulfur stable zone in a solution containing a lower sulfuric acid activity is indeed limited by activity. As |H 2 S(aq)| decreases, E of formula (h) rises to a more positive value at a given pH. As |SO 4 2 - | or |HSO 4 - | decreases, the E of equations (d) and (e) drops to less positive values ​​at a given pH. Therefore, it can be seen from the equilibrium line of the material activity of 0.1 and 10 -4 mol∕L in Fig. 1, the stable zone of elemental sulfur is reduced with the increase of activity, and finally disappears into H 2 S(aq) and SO 4 2 - or HSO. 4 - balance line. The dominant zone map indicates the thermodynamically stable zone of matter, but the rate at which some substances reach equilibrium may be slow. For example, although some microorganisms can oxidize elemental sulfur to sulfate, elemental sulfur is quite stable in pure oxygenated water. The oxidation of dissolved sulfide to sulfate can be carried out very quickly, while the reduction of sulfate to sulfide is quite difficult. However, some microorganisms can carry out this reduction and use it as an energy source. Kinetic factors may be very limited in achieving chemical equilibrium, but can often be overcome by using high temperatures (in terms of aqueous standards).
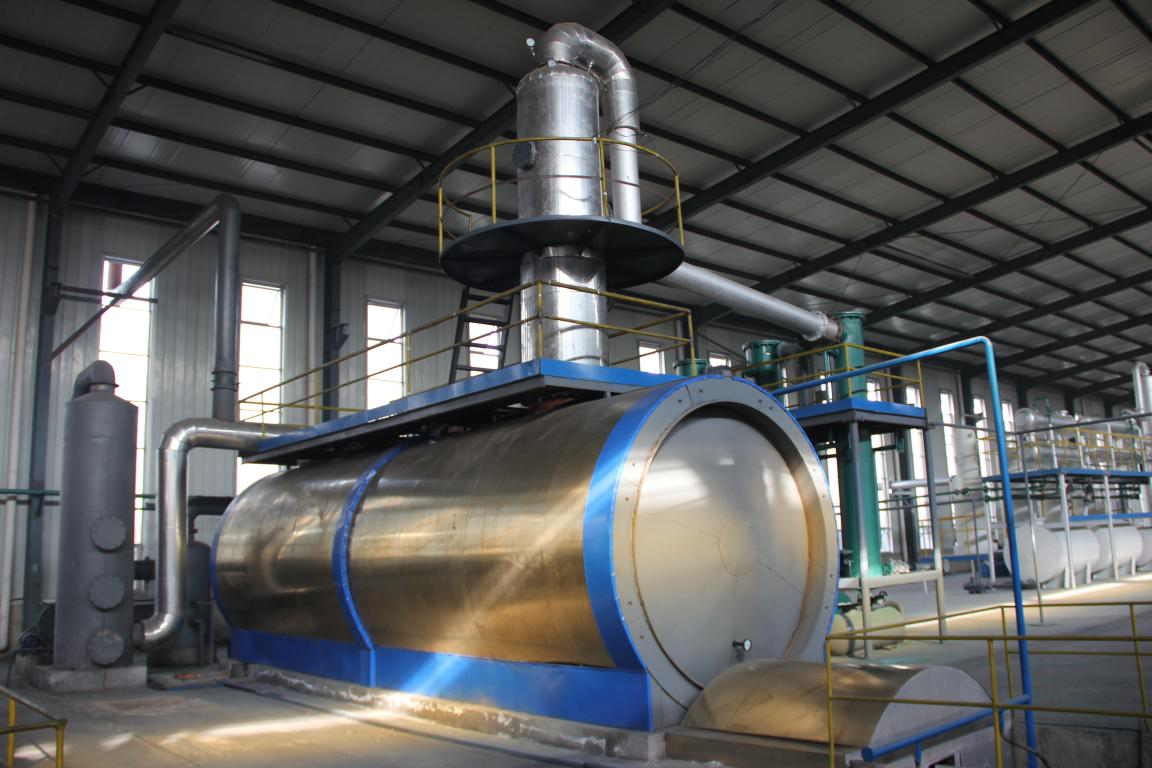
Automatic Type Oil Distillation Plant
The Waste Engine Oil Distillation Plant is used to refine waste engine oil, crude oil and fuel oil after pyrolysis process into diesel grade oil, gasoline or and base oil. The daily capacity of this plant is about 5-6 tons.
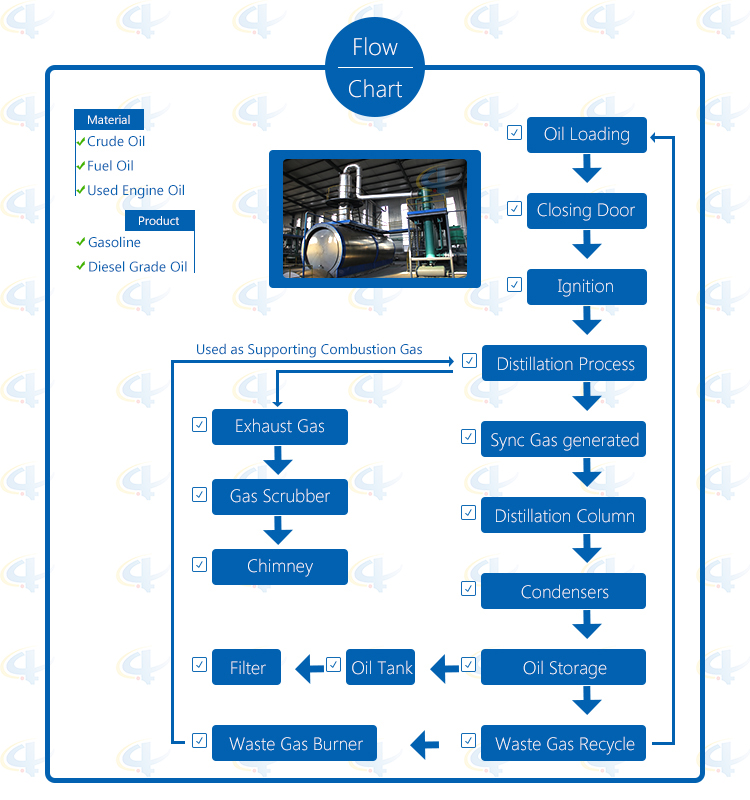
Flow-chat of waste engine oi Distillation Plant
Advantage of waste engine oi distillation plant
1. Unique and original manufacturing and technology with our own formula of our equipments in China;
2. Unique horizontal design, high oil output with about 90% oil yield and 100% conversion rate, highly effective and profitable;
3. Good quality end product oil as the substitution of standard diesel oil in usage;
Automatic submerged welding technology, ultrasonic nondestructive testing, both manual and the automatic safety devices;
4. Sync gas recycling system: fully burned after recycling and utilization, saving fuel and preventing pollution;
5. National patent, unique heat insulation shell: high efficiency temperature keeping, excellent energy-saving effect;
6. High condensing efficiency condensers with more oil output. Good quality oil, longer lifetime, and easy to clean;
7. National patent water film smoke scrubbers: efficient removal of the acid gas and dust of the smoke, environmental friendly to meet related national standards.
Technical Parameter of Waste engine Oil Distillation Plant
NO.
Item
Technical Parameter
1
Suitable Raw Materials
Waste engine oil, Pyrolysis fuel oil, crude oil
2
Structure
Horizontal Type
3
Capacity(24 hours)
3.5-6.5Mt
4
Work Pressure
Normal Pressure
5
Oil Yield
80%-90%
6
Power
18 kw/H
7
Cooling Method
Cycle water
8
Condensers
4 pieces of Vertical condensers
9
Emission Treatment
New DE-sulfurization Smoke Scrubbers
10
Heating Method
Hot Air
11
Type of Installation
With Foundation
12
Noise dB(A)
≤85
13
Dimension of Reactor(mm)
Ф2200×6000
Ф2500×8800
14
Operating Mode
Semi-continuous Operation
15
Main Chamber Weight (MT)
10~13Mt
16
Total Weight(MT)
25~35Mt
17
Installation Space Required
35m*15m
18
End Product
Non-standard diesel oil
19
Manpower
1~2/shift
20
Shipment Requirement
2*40HC=Ф2200×6000
1*40HC+1*40FR=Ф2500×8800
Automatic Type Oil Distillation Plant Automatic Type Oil Distillation Plant,Automatic Type Waste Oil Distillation Plant,Used Engine Oil Refining Machine,Automatic Waste Oil Distillation Plant Shangqiu Jinpeng Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.recyclings.nl